- English
- فارسی
Embedding CuO Nanoparticles in PDMS-SiO2 Coating to Improve Antibacterial Characteristic and Corrosion Resistance
Shima Tavakoli, Shervin Nemati, Mahshid Kharaziha, Safoura Akbari-Alavijeh
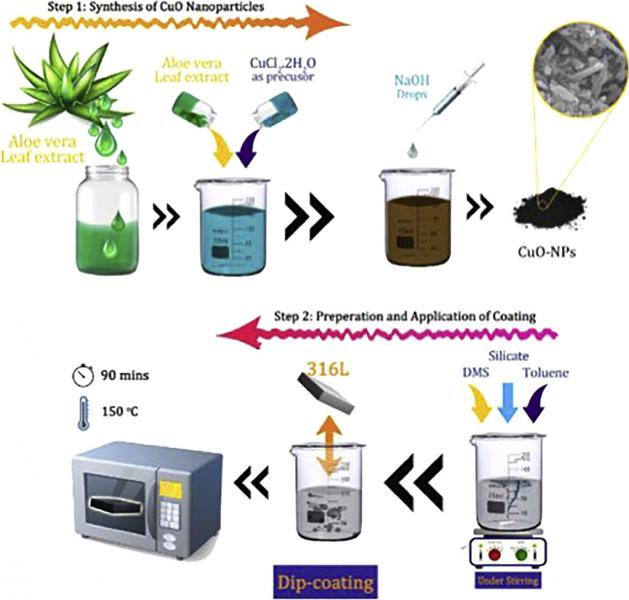
The purpose of this paper was to develop the hydrophobic nanocomposite coatings of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-SiO2-CuO to improve biocompatibility, corrosion resistance and antibacterial property of 316 L stainless. In this research, after synthesize of CuO and SiO2 nanopowders using wet-chemical approaches, PDMS-SiO2-CuO coatings consisting of various amounts of CuO nanoparticles were developed using dip-coating process. The nanocomposite coatings were characterized with regard to the structural and physical properties, corrosion resistance, antibacterial activity and cellular interactive responses. The results showed that incorporation of CuO nanoparticles <2 wt% improved the corrosion resistance of 316 L stainless steel. At higher CuO nanoparticle contents (>1 wt%), the agglomeration of nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects resulted in reduced antibacterial characteristics and MG63 cell viability and proliferation. In summary, PDMS-SiO2-CuO nanocomposite coating with significant antibacterial and anticorrosion behavior could be a promising coating for biomedical implants.